User Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Feature List
- Public Parameters for Tasks and Events
- Common Arguments
- Quick start
- Features
- FAQ
- Command Summary
![]() Note:
Note:
The name SOChedule is case-insensitive in the text and images in this User Guide.
i.e. SOChedule, SoChedule, Sochedule can be used interchangeably.
Introduction
SOChedule is a one-stop solution for NUS School of Computing (SoC) students to manage their tasks and events effectively. Targeted at users who can type fast and prefer typing to mouse input, SOChedule is optimized for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI).
Feature List
General Commands
Task-Specific Commands
- Adding a task:
add_task - Deleting a task:
delete_task - Editing a task:
edit_task - Listing all tasks:
list_task - Marking one or more tasks as done :
done_task - Marking a task as uncompleted :
undone_task - Getting today’s tasks:
today_task - Finding tasks by name:
find_task - Sorting all tasks:
sort_task - Pinning a task:
pin_task - Unpinning a task:
unpin_task - Clearing completed tasks:
clear_completed_task - Clearing expired tasks:
clear_expired_task
Event-Specific Commands
- Adding an event:
add_event - Deleting an event:
delete_event - Editing an event:
edit_event - Listing all events:
list_event - Getting today’s events:
today_event - Finding events by name:
find_event - Clearing expired events:
clear_expired_event - Finding free time slots:
free_time
Commands Related to Both Task and Event
- Finding schedule given a date:
find_schedule - Summarising tasks and events completion status:
summary - Clearing SOChedule:
clear
Public Parameters for Tasks and Events
As listed below are the attributes to be specified for Tasks and Events. All parameters are mandatory unless otherwise stated.
Common to both Task and Event
| Attribute | Identifier | Restriction(s) |
|---|---|---|
Name |
n/ |
|
Category |
c/ |
|
Tag |
t/ |
|
Task-Specific
| Attribute | Identifier | Restriction(s) |
|---|---|---|
Deadline |
d/ |
|
Priority |
p/ |
|
Event-Specific
| Attribute | Identifier | Restriction(s) |
|---|---|---|
Start Date |
sd/ |
|
End Date |
ed/ |
|
Start Time |
st/ |
|
End Time |
et/ |
|
Common Arguments
Below are a few arguments commonly found in SOChedule commands, and their corresponding restrictions, command-specific restrictions notwithstanding. Breaking any of the below restrictions will result in a invalid command format error.
| Attribute | Restriction(s) | Used in | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
INDEX |
|
|
Valid:
|
Date-related arguments
|
|
|
Valid:
|
Time-related arguments
|
|
|
Valid:
|
Quick start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
SOChedule.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your SOChedule.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. A sample SOChedule is given below. There would not be pre-entered data on first launch so that users start using immediately.
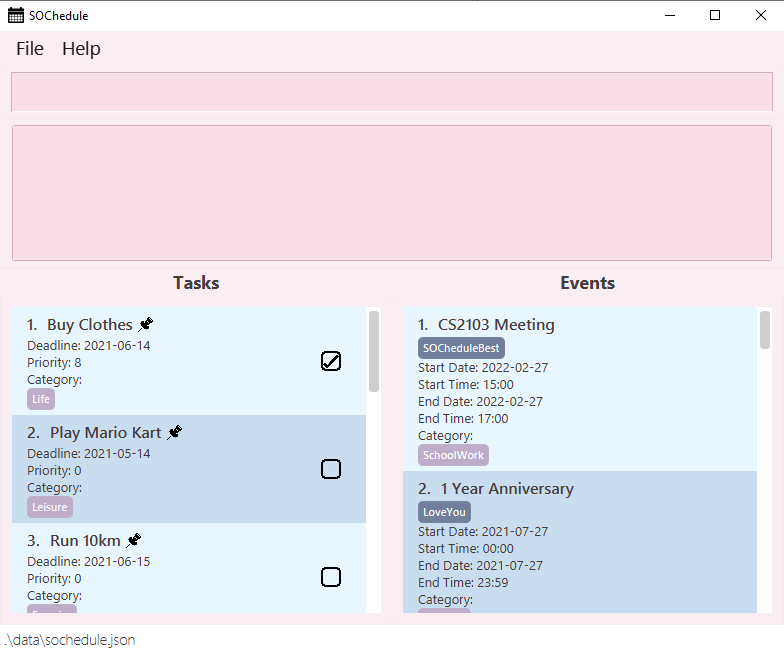
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try:-
list_task: Lists all tasks. -
add_taskn/CS2103 assignment d/2022-04-07 p/1 c/schoolwork t/urgent: Adds a task namedCS2103 assignmentto the SOChedule with its respective attributes. Please verify the validity of the date parameter. -
delete_task3: Deletes the 3rd task shown in the current list. -
exit: Exits the app.
-
-
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Features
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user.
e.g. inundone_task INDEX,INDEXis a parameter which can be used asundone_task 1. -
Items in square brackets are optional.
e.gn/TASKNAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/Quiz t/CS2103or asn/Quiz. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times.
e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used ast/friend,t/friend t/familyetc. -
If a parameter is expected only once in the command, but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be taken.
e.g. if you specifyp/1 p/2, onlyp/2will be taken. -
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
list_task,list_event) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifieslist_task 123, it will be interpreted aslist_task.
Viewing help: help
Shows a message explaining how to access the help page.
Exiting the program: exit
Exits the program.
Adding a task: add_task
Adds a task into the task list.
Format: add_task n/TASKNAME d/DEADLINE p/PRIORITY [c/CATEGORY]... [t/TAG]...
-
n/is followed by the task name, it is case-sensitive. -
d/is followed by the date of deadline, with the formatYYYY-MM-DD.
Deadline cannot be a past date. -
p/is followed by the priority, with 0 being highest and 9 being lowest.
Other inputs are not accepted. -
c/is followed by the category. Different categories are separated by white space (e.g.c/c1 c/c2).
It is optional. -
t/is followed by the tag. Different tags are separated by white space (e.g.t/t1 t/t2).
It is optional.
![]() Note:
Note:
- Any valid prefixes and input arguments (e.g.
n/Homework 1orp/1) followed by invalid prefixes and input arguments (e.g.name/Name,tag/TagorT&sk) will lead to an error. - If the same prefix (excluding
c/,t/) appears multiple times in the input (e.g.n/n1 n/n2 n/n3), only the last occurrence would be taken (i.e.n/n3).
Examples:
-
add_task n/CS2103 assignment d/2022-02-27 p/1 c/schoolwork t/urgentadds a new task named “CS2103 assignment” with the respective parameters. -
add_task n/CCA admin work d/2022-02-28 p/2 c/CCAadds a new task “CCA admin work” with the respective parameters.
Deleting a task: delete_task
Deletes a task from the task list.
Format: delete_task INDEX
- Deletes the task at the specified INDEX.
- The
INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the currently displayed task list.
Examples:
-
list_taskfollowed bydelete_task 2deletes the second task in the full task list. -
find_task homeworkfollowed bydelete_task 1deletes the first task in the result of thefind_taskcommand.
Editing a task: edit_task
Edits an existing and uncompleted task in the task list.
Format: edit_task INDEX [n/TASKNAME] [d/DEADLINE] [p/PRIORITY] [c/CATEGORY]... [t/TAG]...
- Edits the task at the specified
INDEX. - Only an existing and uncompleted task can be edited.
(i.e. Completed tasks cannot be edited) - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
-
DEADLINEprovided cannot be a past date. - When editing tags/categories, the existing tags/categories of the task will be removed.
(i.e. adding of tags/categories is not cumulative) - Edited task cannot be the same as the original task or equivalent to another existing task in the task list.
Same tasks means the name, priority, deadline, tags (if any) and categories (if any) of two tasks are equal. - When editing tags and categories, the order given in the input and the order as shown in the UI can be different.
For example, in inputedit_task 1 t/t2 t/t10,t/t2is beforet/t10in the input, butt10may appear in the UI beforet2. Lexicographical order is followed.
![]() Note:
Note:
-
Any valid prefixes and input arguments (e.g.
n/Homework 1orp/1) followed by invalid prefixes and input arguments (e.g.name/Name,tag/TagorT&sk) will lead to an error. -
You can remove all the task’s tags by typing
t/without specifying any tags after it.
Similarly, you can remove all the task’s categories by typingc/without specifying any categories after it -
If the same prefix (excluding
c/,t/) appears multiple times in the input (e.g.n/n1n/n2), the latter one would be taken (i.e.n/n2).
Examples:
-
edit_task 1 n/t1edits the name of the first task (if present in SOChedule) to beeditedTaskName. -
edit_task 2 p/3 t/edits the priority of the second task (if present in SOChedule) to be3and clears all existing tags.
Illustration of usage of edit_task:
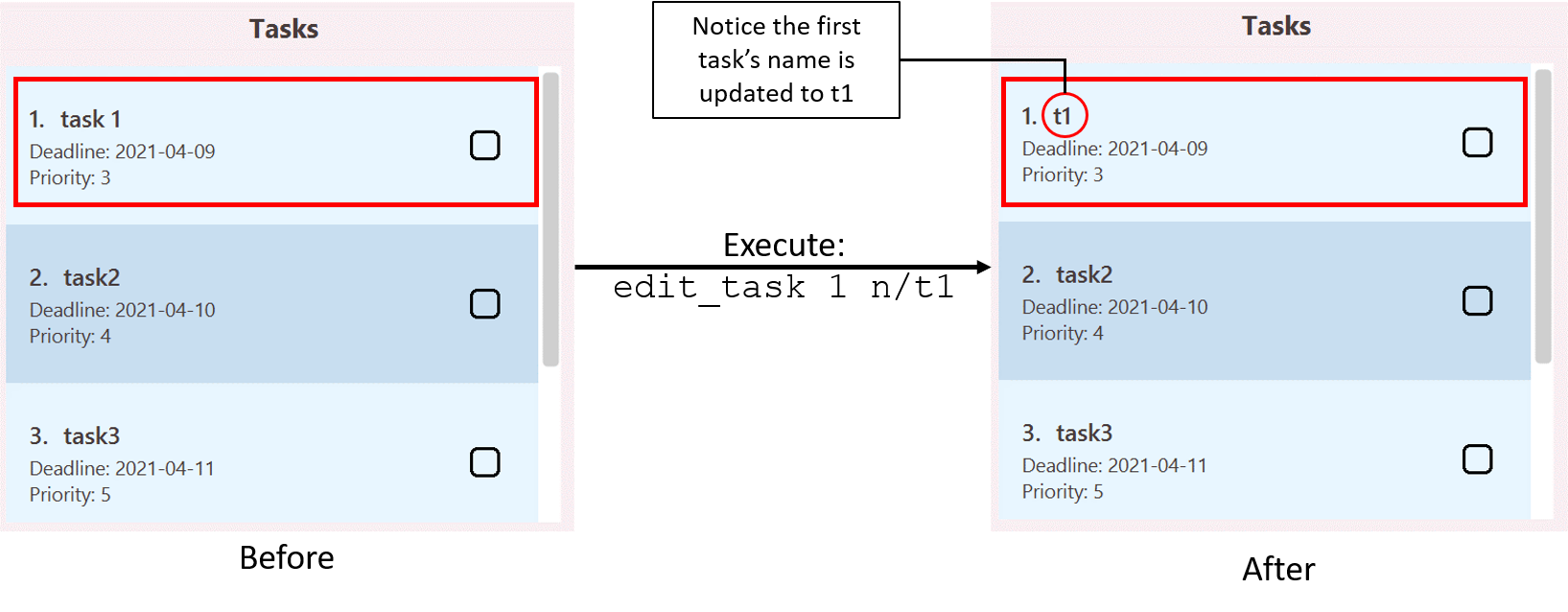
Listing all tasks: list_task
Lists all tasks from the task list.
Format: list_task
Marking one or more tasks as done: done_task
Marks one or more task from the task list as completed.
Format: done_task INDEX1 [INDEX2] ...
- Marks the task(s) at the specified INDEX(es) as completed.
- Specified task(s) must not be completed.
- Multiple indices are to be separated by a whitespace, e.g.
1 2. - All specified tasks must be uncompleted and existing before calling this command.
-
Duplicate indices are not allowed.
Otherwise, an error message indicating invalid command format will be returned.
![]() Note:
Note:
- If indices provided include both an index for a task not existing in task list and an index for a completed task, the error message will only be about the non-existing task.
Examples:
-
done_task 1 2marks the first and second task in the task list as completed.
Illustration of usage of done_task:
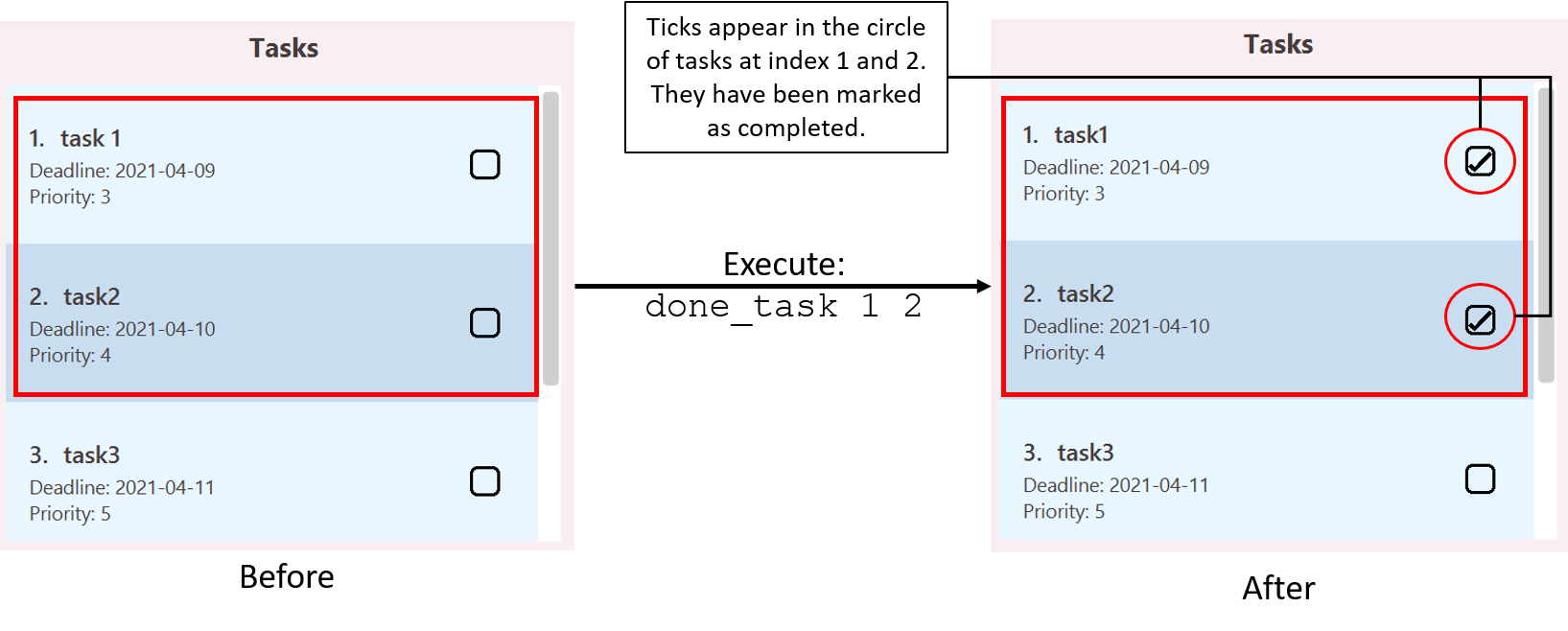
Marking a task as uncompleted: undone_task
Marks a completed task from the task list as uncompleted.
Format: undone_task INDEX
- Marks the task at the specified INDEX as uncompleted.
- Specified task must be complete.
Examples:
-
undone_task 1marks the first task in the task list as uncompleted.
Illustration of usage of undone_task:

Getting today’s tasks: today_task
Lists all tasks that have deadline on today from the task list.
Format: today_task
Finding tasks by name: find_task
Finds tasks whose names contain any of the given keywords from the task list.
Format: find_task KEYWORD1 [KEYWORD2] ...
- The search is case-insensitive, e.g.
homeworkwill matchHomework. - The search scope is the full task list.
- The order of the keywords does not matter.
E.g.Practice Problemswill matchProblems Practice. - Only the name of the tasks is searched.
- Only full words will be matched. E.g.
CSwill not matchCS2103. - Tasks matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch).
E.g.CS2103 Homeworkwill returnST2131 Homework,CS2103 Quiz.
Examples:
-
find_task Homeworkreturnsst2131 homeworkandHomework 1 -
find_task assignment homeworkreturnsAssignment 1,Homework 2
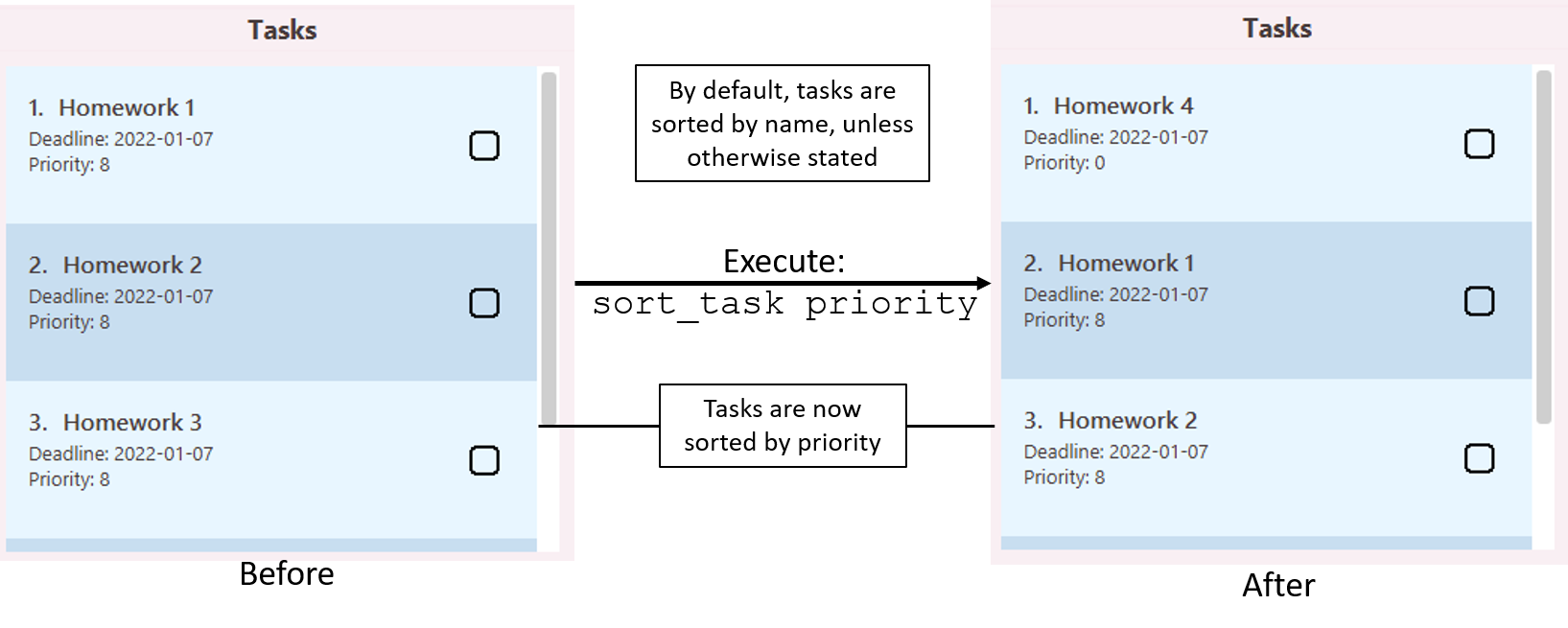
Sorting all tasks: sort_task
Sorts the task list.
Format: sort_task ARGUMENT
- Sorts task list and updates UI based on supplied argument.
- Accepted arguments (case-sensitive):
-
name: Sorts by task name, in increasing lexicographical order -
deadline: Sorts by task deadline, in increasing date order -
completion: Sorts by task completion status, with completed tasks at the bottom -
priority: Sorts by task priority, in decreasing order, from priority 0 on top, to priority 9 at the bottom
-
- On subsequent boots, the following will happen:
- Relative order from previous launch will be preserved.
- However, if any order-altering command (
pin_task,unpin_task, andfind_task) is issued, tasks will be sorted by name by default, unless otherwise stated by anothersort_taskcommand. - Marking a task as complete (
done_task) or incomplete (undone_task) or adding (add_task) and editing (edit_task) tasks does not constitute an order-altering command.
Examples:
-
sort_task completionsorts the task list by completion status. -
sort_task namesorts the task list by name.
Illustration of usage of sort_task:
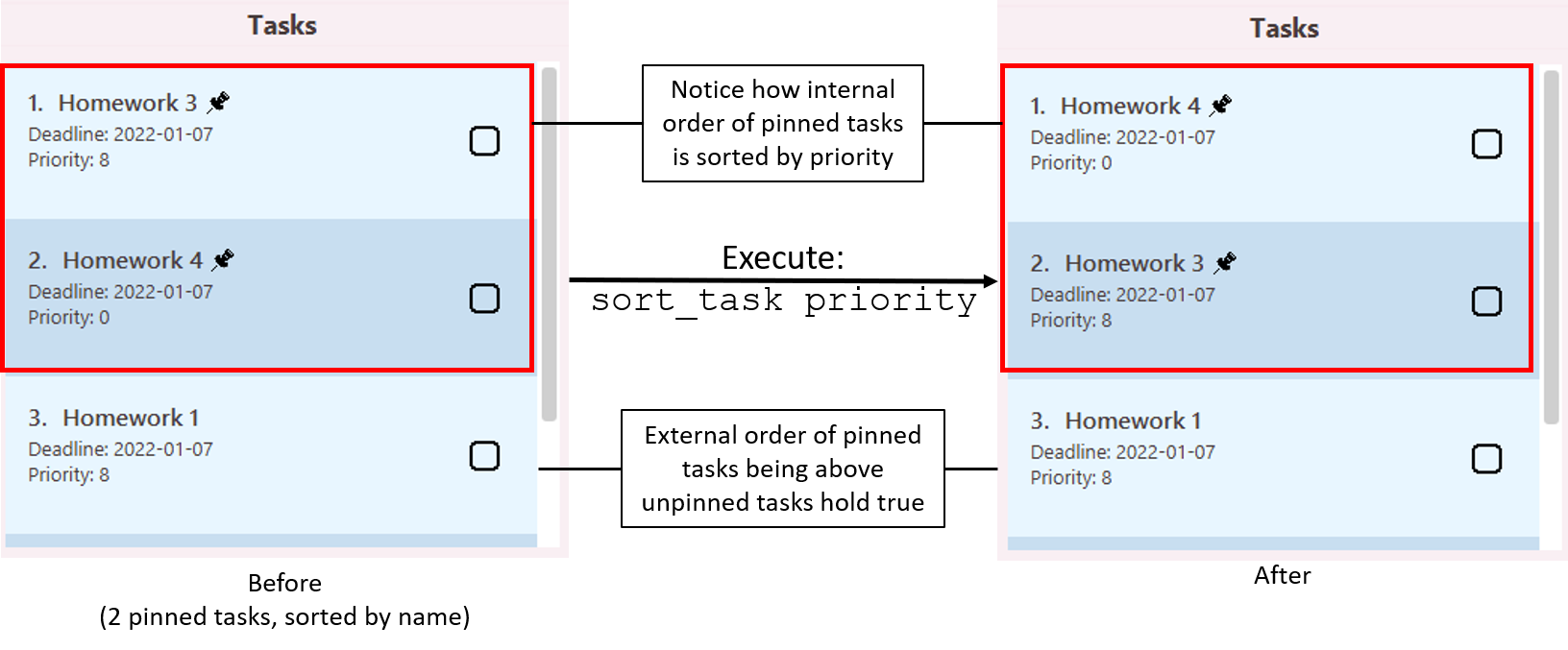
Pinning a task: pin_task
Pins a task from the task list.
Format: pin_task INDEX
- Pins the task at the specified INDEX.
- Already pinned tasks will be unable to be pinned a second time.
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed task list.
- After pinning, the Task List will be sorted either according to previously entered
sort_taskcommand, or name (by default). See here.- Should there be two or more pinned tasks, the pinned tasks will be sorted as well.
- Only the fact that pinned tasks will appear over the unpinned tasks is guaranteed.
Internal order of pinned tasks is not persistent oversort_task.
- Pinned tasks are persistent over instances of SOChedule.
Examples:
-
pin_task 1pins the first task in the task list
Illustration of usage of pin_task:

Illustration of the interaction between pin_task and sort_task:
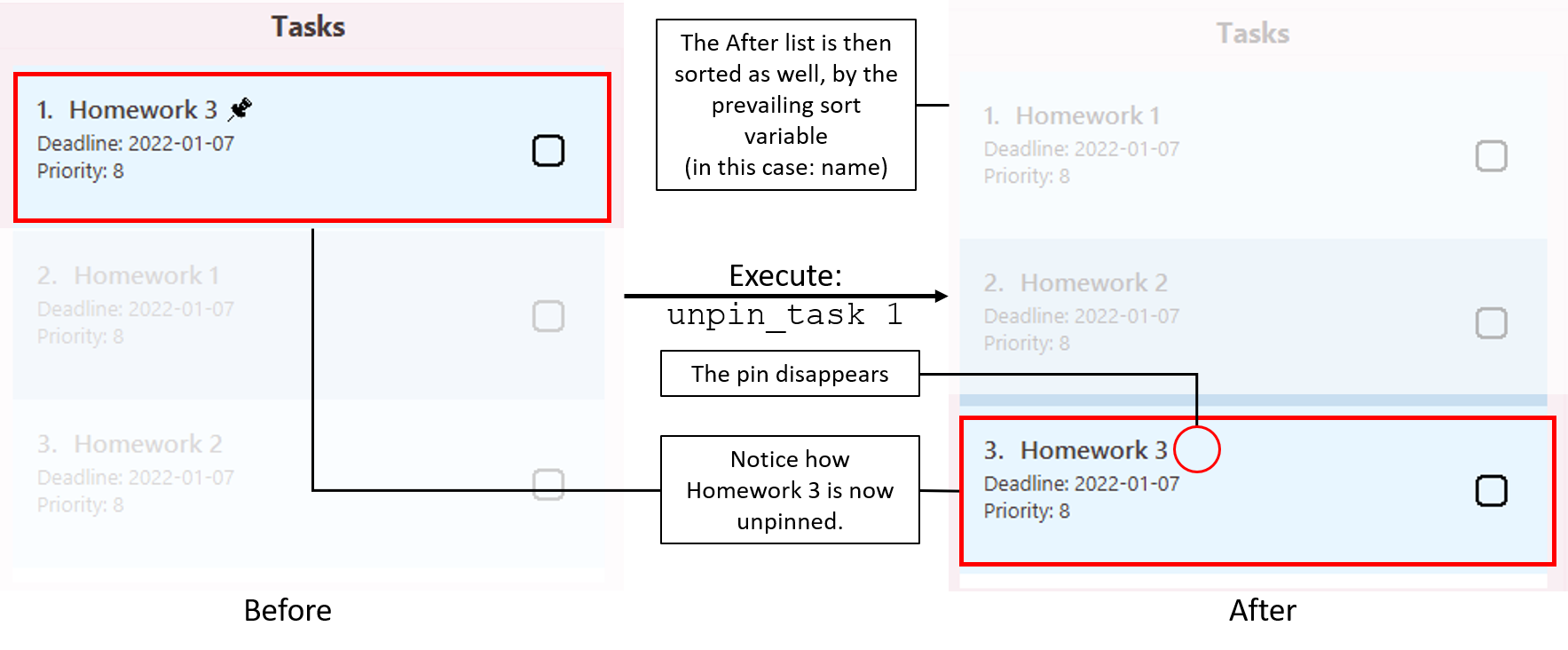
Unpinning a task: unpin_task
Unpins a task from the task list.
Format: unpin_task INDEX
- Unpins the task at the specified INDEX.
- Follows similar restrictions to
pin_task.
Examples:
-
unpin_task 1unpins the first task in the task list
Illustration of usage of unpin_task:
Clearing completed tasks: clear_completed_task
Clears tasks marked as completed from the task list.
Format: clear_completed_task
![]() Note:
Note:
- This command is still able to be executed on a task list without any completed tasks.
In this case, success messageCompleted tasks (if any) have been cleared!will still be displayed.
However, no tasks will be cleared since there are no completed tasks.
Illustration of usage of clear_completed_task:
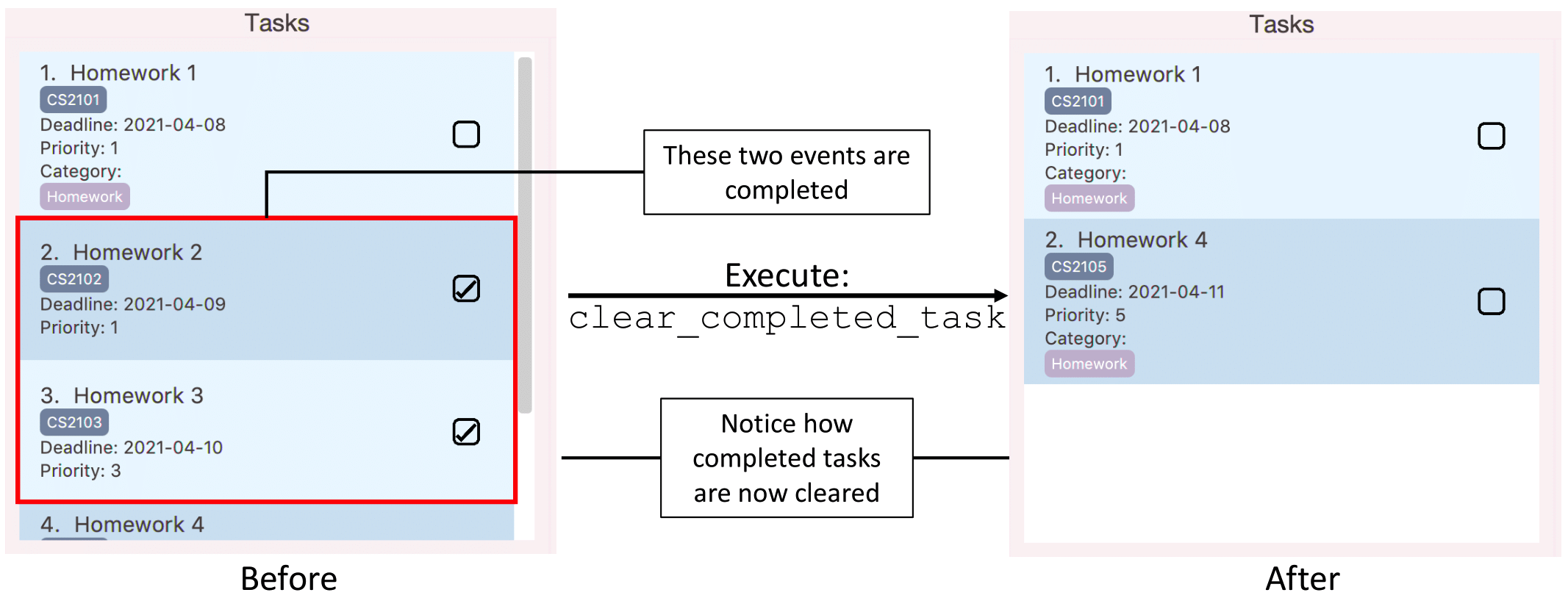
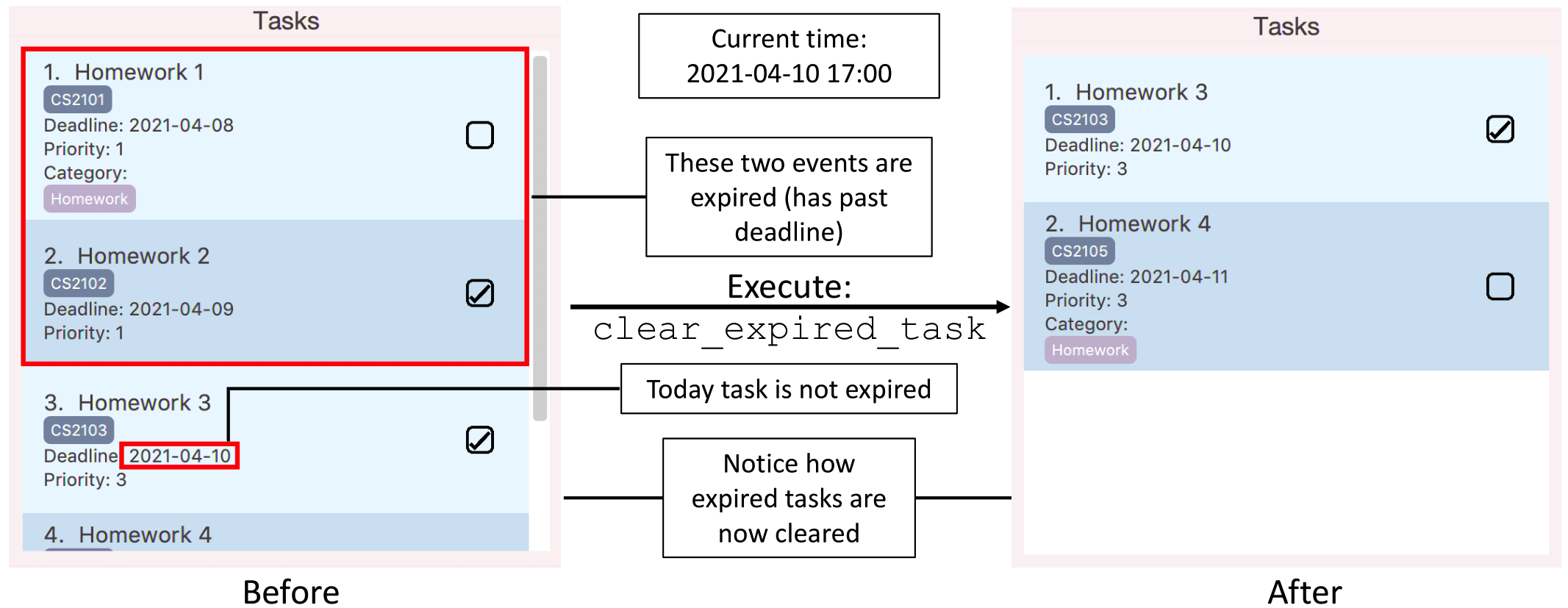
Clearing expired tasks: clear_expired_task
Clear tasks with past deadlines from the task list.
Format: clear_expired_task
- For a task to be considered expired, the task’s
deadlineshould be an earlier date as compared to the local date on the user’s computer.
Hence, changing of date on a computer could affect the judgement of expiration.
![]() Note:
Note:
- This command is still able to be executed on a task list without any expired tasks.
In this case, success messageExpired tasks (if any) have been cleared!will still be displayed.
However, no tasks will be cleared since there are no expired tasks.
Illustration of usage of clear_expired_task:
Adding an event: add_event
Adds an event to the event list.
Format: add_event n/EVENTNAME sd/STARTDATE st/STARTTIME ed/ENDDATE et/ENDTIME [c/CATEGORY]... [t/TAG]...
-
n/is followed by the event name, it is case-sensitive. -
sd/is followed by the starting date, in the format of YYYY-MM-DD. -
st/is followed by the starting time in the 24-hour format and in the format of hh:mm -
ed/is followed by the ending date. -
et/is followed by the ending time in the 24-hour format. - The
ENDDATEandENDTIMEprovided must be afterSTARTDATEandSTARTTIME. - The
ENDDATEandENDTIMEprovided cannot be a past date and time. -
c/is followed by the category. Different categories are separated by white space (e.g.c/c1 c/c2).
It is optional. -
t/is followed by the tag. Different tags are separated by white space (e.g.t/t1 t/t2).
It is optional.
![]() Note:
Note:
-
The
STARTDATEandSTARTTIMEprovided can be in the past for ongoing events. -
Events that overlap in date and time are allowed.
-
Any valid prefixes and input arguments (e.g.
n/Meeting 1orst/14:00) followed by invalid prefixes and input arguments (e.g.name/Name,tag/TagorE@ent) will lead to an error. -
If the same prefix (excluding
c/,t/) appears multiple times in the input (e.g.n/n1 n/n2 n/n3), only the last occurrence would be taken (i.e.n/n3).
Examples:
-
add_event n/CS2103 meeting sd/2021-05-27 st/15:00 ed/2022-02-27 et/17:00adds an event with nameCS2103and its respective attributes to the event list.
Deleting an event: delete_event
Deletes an event from the event list.
Format: delete_event INDEX
- Deletes the event at the specified INDEX.
- Note that only one
INDEXis accepted, multipleINDEXwill lead to input format error. - The
INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed event list.
Examples:
-
delete_event 3deletes the third event from the event list.
Editing an event: edit_event
Edits an existing and unexpired event in the event list.
Format: edit_event INDEX [n/EVENTNAME] [sd/STARTDATE] [st/STARTTIME] [ed/ENDDATE] [et/ENDTIME] [c/CATEGORY]... [t/TAG]...
- Edits the event at the specified
INDEX. - An expired event could only be edited when users edit the past end date and time to an unexpired end date and time (i.e. to extend the event).
- Except the condition above, only unexpired event can be edited.
- At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- The
ENDDATEandENDTIMEprovided must be afterSTARTDATEandSTARTTIME. - The
ENDDATEandENDTIMEprovided cannot be a past date and time. - When editing tags/categories, the existing tags/categories of the event will be removed.
(i.e. adding of tags/categories is not cumulative) - When editing tags and categories, the order given in the input and the order as shown in the UI can be different.
For example, in inputedit_event 1 t/tag1 t/tag2,t/tag1is beforet/tag2, buttag2may appear in the UI beforetag1.
![]() Note:
Note:
-
The
STARTDATEandSTARTTIMEprovided can be in the past for ongoing events. -
Events that overlap in date and time are allowed.
-
Any valid prefixes and input arguments (e.g.
n/Meetingorst/00:00) followed by invalid prefixes and input arguments (e.g.name/Name,tag/TagorE@ent) will lead to an error. -
You can remove all the event’s tags by typing
t/without specifying any tags after it.
Similarly, you can remove all the event’s categories by typingc/without specifying any categories after it -
If the same prefix (excluding
c/,t/) appears multiple times in the input (e.g.n/n1n/n2), the latter one would be taken (i.e.n/n2).
Examples:
-
edit_event 1 n/editedEventNameedits the name of the first event (if present in the event list) to beeditedEventName. -
edit_event 2 sd/2021-03-18 t/edits the start date of the second event (if present in the event list) to be2021-03-18and clears all existing tags.
Listing all events: list_event
Lists all events from the event list.
Format: list_event
Getting today’s events: today_event
Lists all events whose duration have overlap with today from the event list.
Format: today_event
Finding events by name: find_event
Finds events whose names contain any of the given keywords from the event list.
Format: find_event KEYWORD1 [KEYWORD2] ...
- The search is case-insensitive, e.g.
meetingwill matchMeeting. - The search scope is the full task list.
- The order of the keywords does not matter.
E.g.Attending Lecturewill matchLecture Attending. - Only the name of the events is searched.
- Only full words will be matched. E.g.
CSwill not matchCS2103. - Events matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch).
E.g.CS2103 Meetingwill returnProject Meeting,CS2103 Lecture.
Examples:
-
find_event Meetingreturnsproject meetingandResearch Meeting. -
find_event talk competitionreturnsCareer Talk,Coding Competition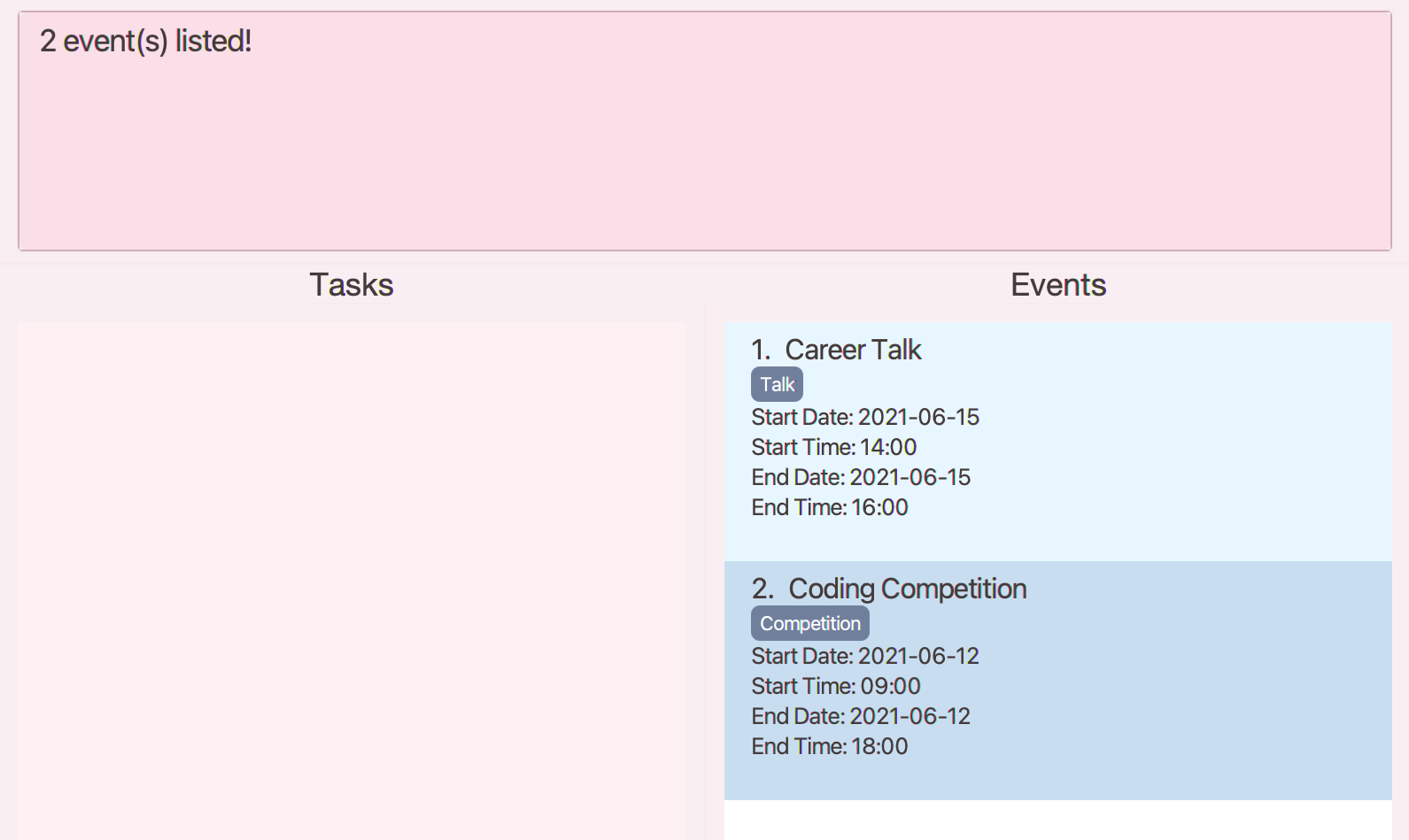
Clearing expired events: clear_expired_event
Clears events with past end date time from the event list.
Format: clear_expired_event
- For an event to be considered expired, the event should have earlier end date and time as compared to the local time on the user’s computer.
Hence, changing of timing on a computer could affect the judgement of expiration.
![]() Note:
Note:
- This command is still able to be executed on a event list without any expired event.
In this case, success messageExpired events (if any) have been cleared!will still be displayed.
However, no event will be cleared since there are no expired event.
Illustration of usage of clear_expired_event:
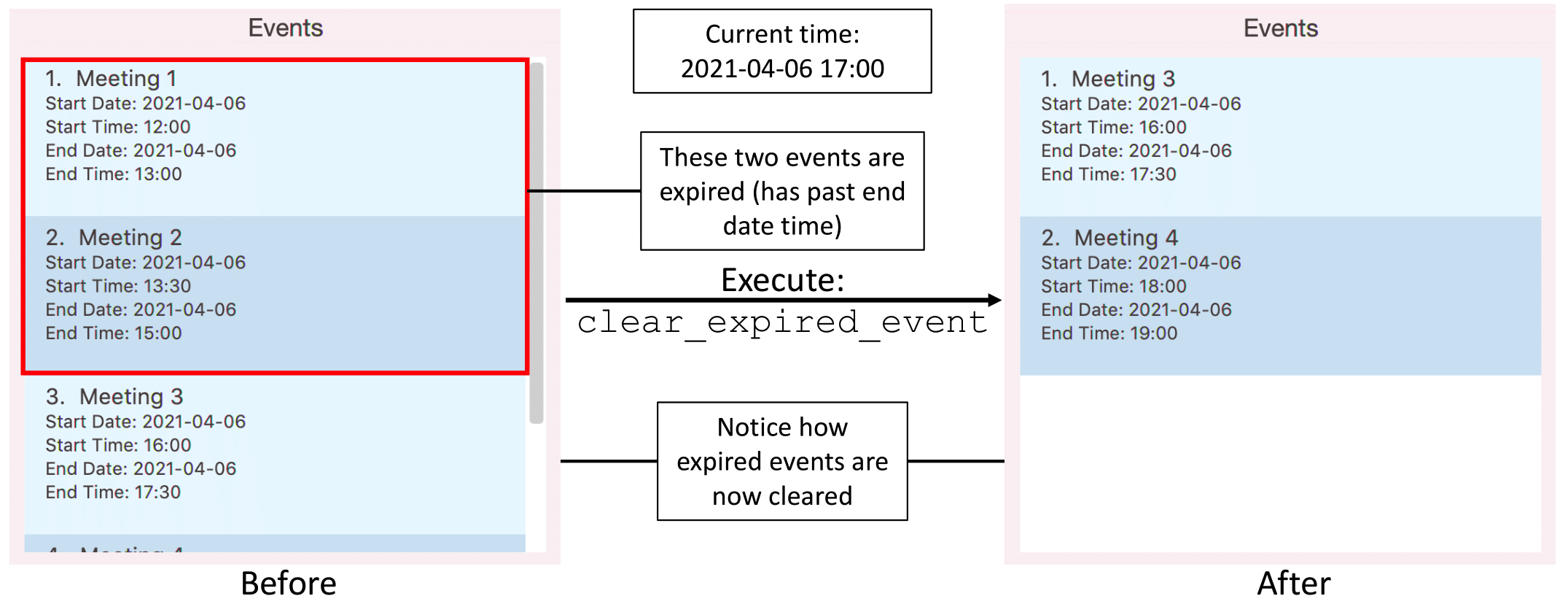
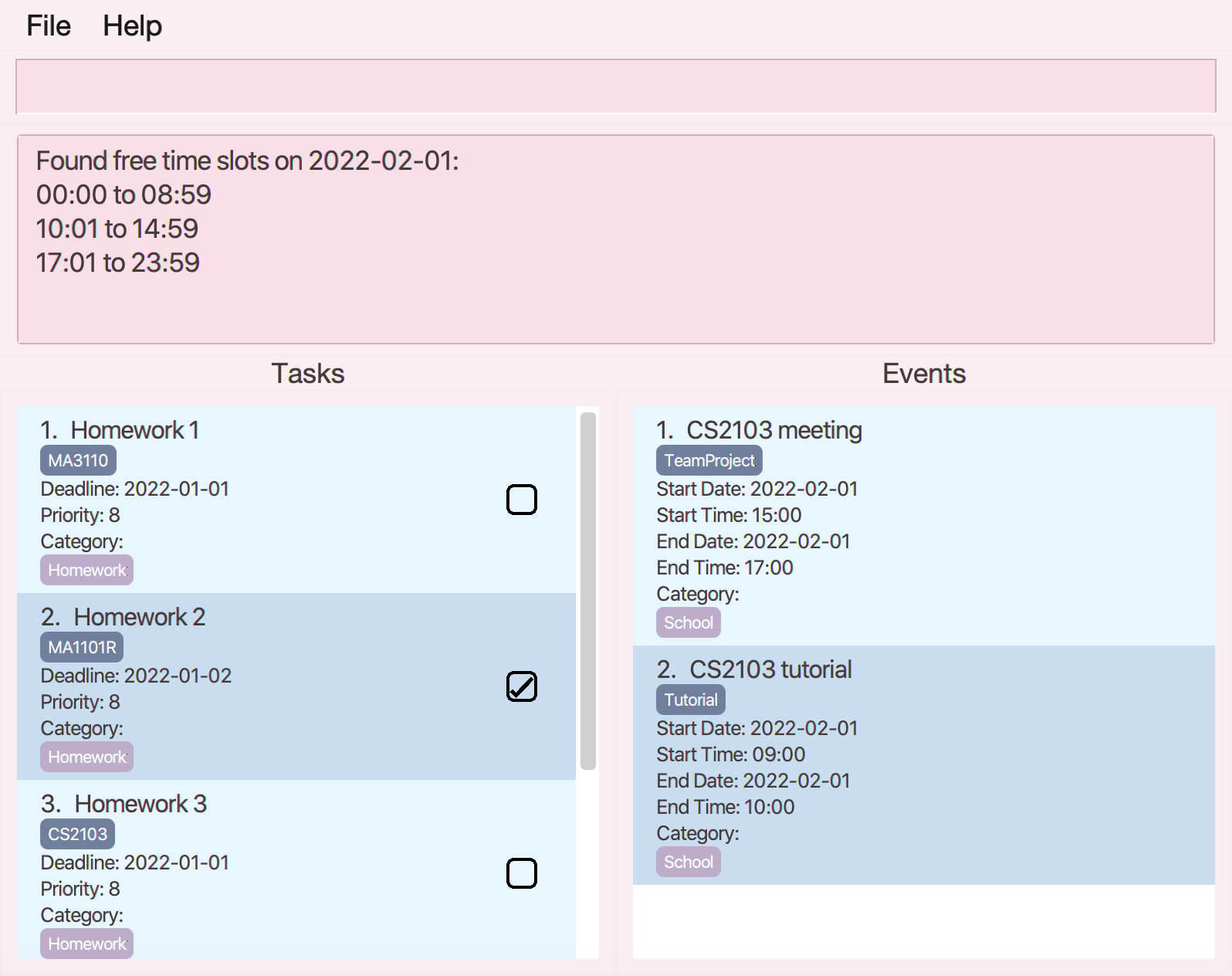
Finding free time slots: free_time
Finds all free time slots on the given date from the event list.
Format: free_time DATE
- Free time slots refer to all times in the given date without any ongoing event.
- Date entered must be a valid date and in the format of
YYYY-MM-DD. - Date entered must be a date from current date onwards.
- Only one single date can be entered.
Examples:
-
free_time 2022-02-01finds all free time slots on the given date2022-02-01.
Illustration of usage of free_time:
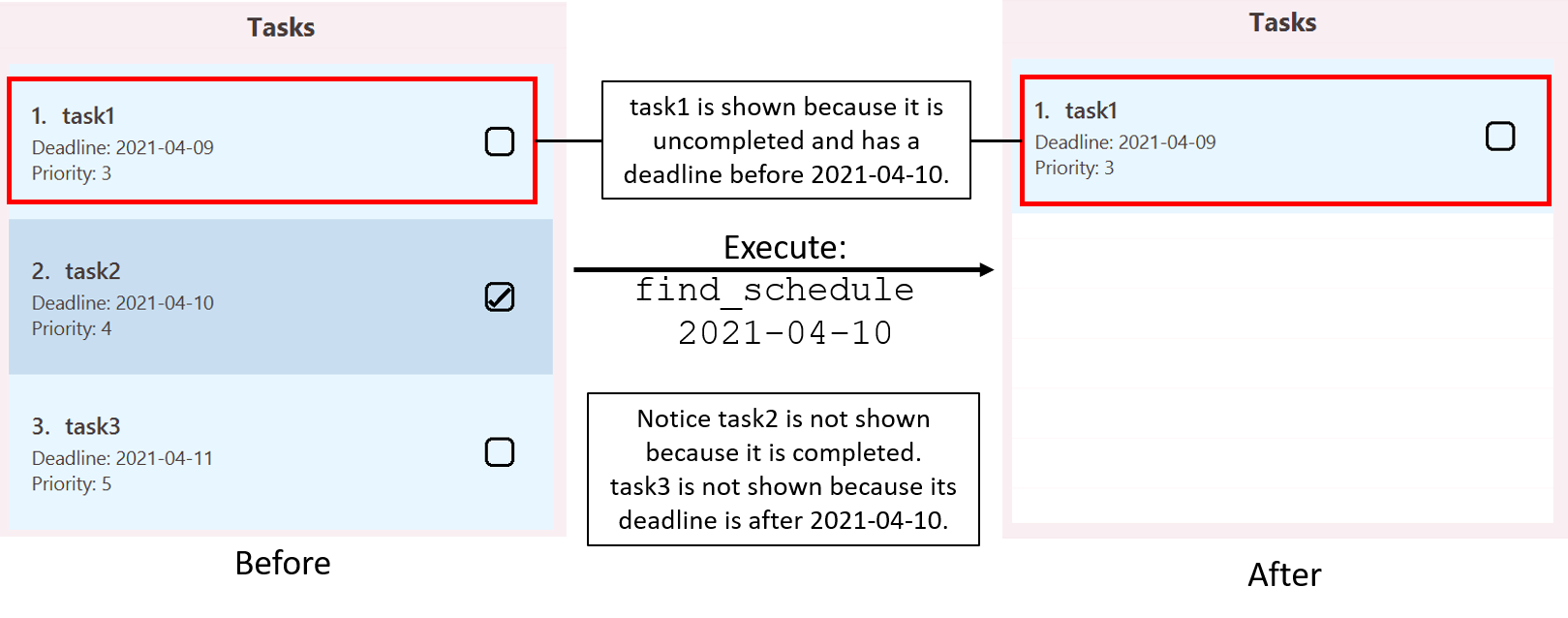
Finding schedule given a date: find_schedule
Given a specified date, finds uncompleted tasks that are due before or on the date and events that are ongoing on the date.
Format: find_schedule DATE
- Tasks found will be incomplete tasks with deadlines before or on the specified date.
- Events found will be events where specified date falls between start date (inclusive) and end date (inclusive).
(i.e. ongoing events) - Date entered must be in the format of
YYYY-MM-DD.
It can be a date that is earlier than today. - Only one single date can be entered.
![]() Note:
Note:
-
After running
find_schedule,list_taskandlist_eventcan be used to display the whole task list and event list respectively. -
This command is still able to be executed on an empty task list, and an empty event list. In this case, the success message will still be displayed.
Examples:
-
find_schedule 2021-04-10finds:- All existing uncompleted tasks with deadlines before or on
2021-04-10. - All existing events where
2021-04-10falls between start date (inclusive) and end date (inclusive).
- All existing uncompleted tasks with deadlines before or on
Illustration of usage of find_schedule:
Due to size constraint, this illustration is split into the before and after view for task list and that for event list.
For task list:
For event list:

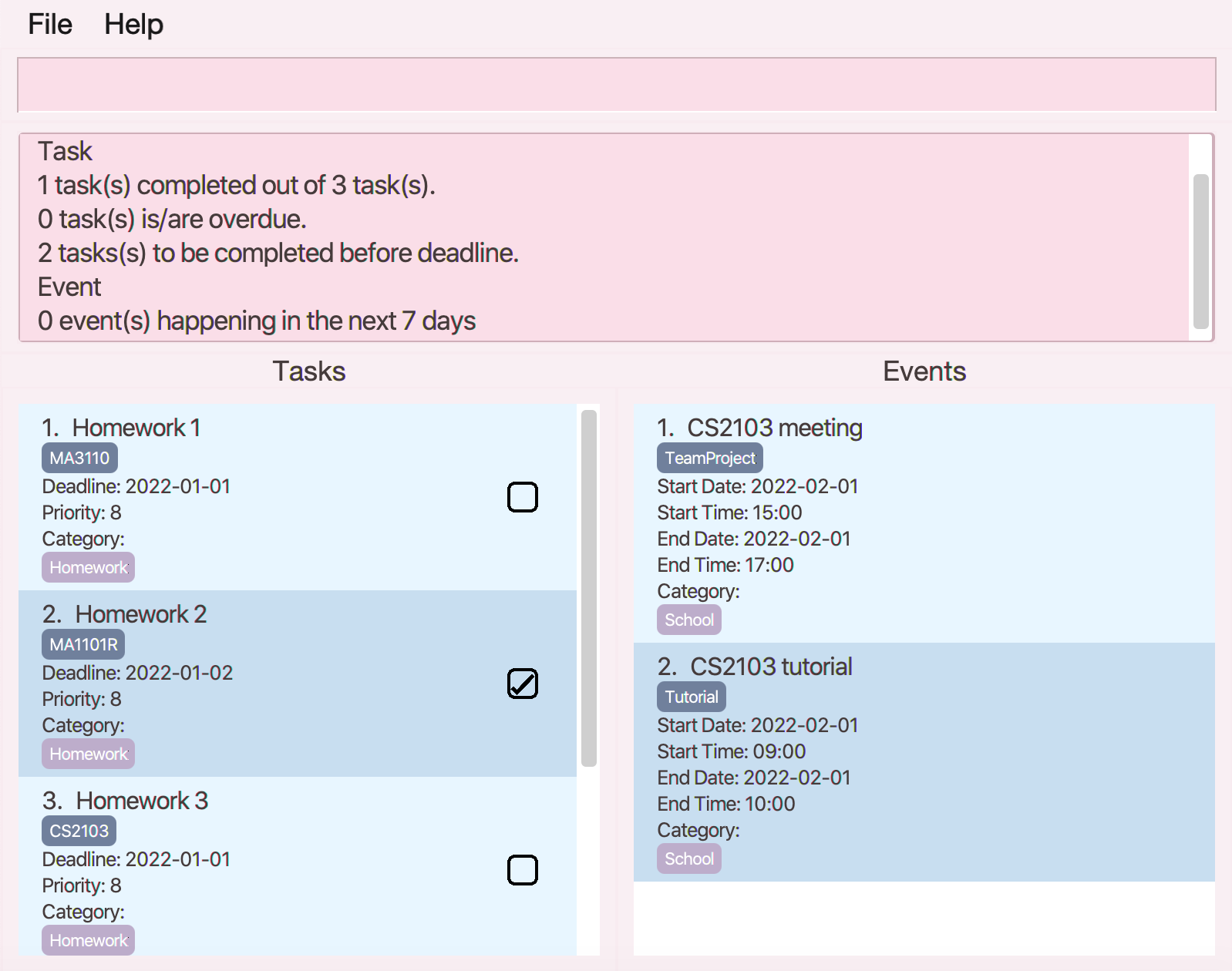
Summarising tasks and events statistics: summary
Displays a summary of tasks completion status and events upcoming for the next 7 days.
Format: summary
- Completed tasks refer to tasks that are done regardless of when the deadline is.
- Overdue tasks refer to incomplete tasks, and current date has passed the deadline.
- Tasks to be completed before deadline refer to incomplete tasks, and current date now has not passed the deadline.
-
Events upcoming in the next 7 days refer to events that are going to happen in the next 7 days.
Events that are happening today are not included.
Illustration of usage of summary:
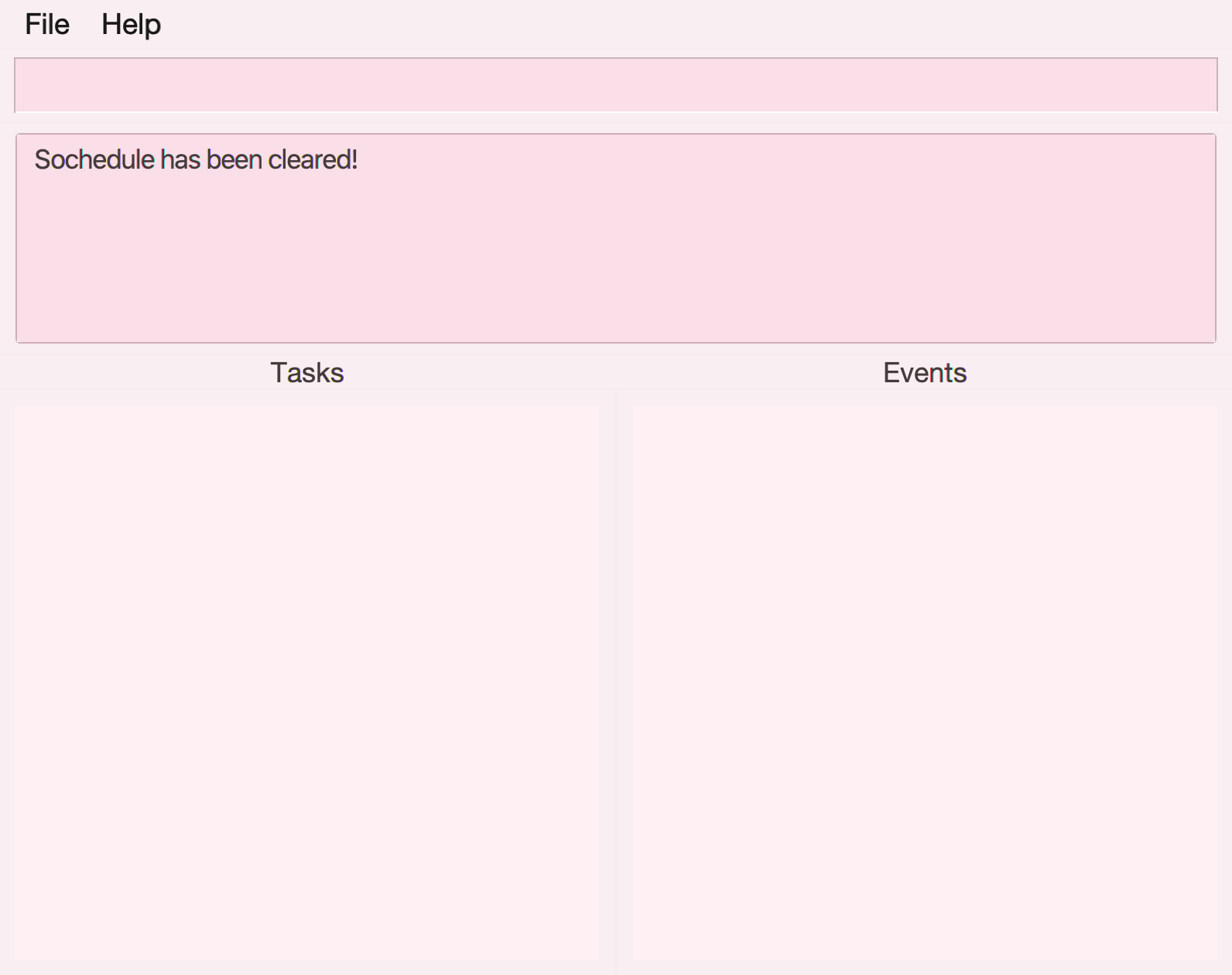
Clearing SOChedule: clear
Clears all tasks and events in the SOChedule’s task list and event list.
Format: clear
Illustration of usage of clear:
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Download the JAR file onto the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous SOChedule home folder (this is contained within the /data folder in the same location as your SOChedule.jar.
Command summary
General commands
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Help | help |
| Exit | exit |
Task-related commands
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Add |
add_task n/TASKNAME d/DEADLINE p/PRIORITY [c/CATEGORY]... [t/TAG]... e.g. add_task n/CS2103 assignment d/2022-02-27 p/1 c/schoolwork t/urgent
|
| Delete |
delete_task INDEXe.g. delete_task 1
|
| Edit |
edit_task INDEX [n/TASKNAME] [d/DEADLINE] [p/PRIORITY] [c/CATEGORY]... [t/TAG]... e.g. edit_task 1 n/editedTaskName
|
| List | list_task |
| Done |
done_task INDEX1 [INDEX2] ...e.g. done_task 1 2
|
| Undone |
undone_task INDEXe.g. undone_task 1
|
| Today | today_task |
| Find |
find_task KEYWORD1 [KEYWORD2] ...e.g. find_task homework
|
| Sort |
sort_task ARGUMENTe.g. sort_task name
|
| Pin |
pin_task INDEXe.g. pin_task 1
|
| Unpin |
unpin_task INDEXe.g. unpin_task 1
|
| Clear Completed | clear_completed_task |
| Clear Expired | clear_expired_task |
Event-related commands
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Add |
add_event n/TASKNAME sd/STARTDATE st/STARTTIME ed/ENDDATE et/ENDTIME [c/CATEGORY]... [t/TAG]...e.g. add_event n/CS2103 meeting sd/2022-02-27 st/15:00 ed/2022-02-27 et/17:00
|
| Delete |
delete_event INDEXe.g. delete_event 3
|
| Edit |
edit_event INDEX [n/EVENTNAME] [sd/STARTDATE] [st/STARTTIME] [ed/ENDDATE] [et/ENDTIME] [c/CATEGORY]... [t/TAG]... e.g. edit_event 1 n/editedEventName
|
| List | list_event |
| Today | today_event |
| Find |
find_event KEYWORD1 [KEYWORD2] ...e.g. find_event meeting
|
| Clear Expired | clear_expired_event |
| Find Free Time |
free_time DATE e.g. free_time 2022-01-01
|
Commands related to both task and event
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Find Schedule |
find_schedule DATE e.g. find_schedule 2022-06-01
|
| Clear Schedule | clear |
| Summary | summary |